What is SPF? The Ultimate Guide to Sun Protection Factor
Confused about SPF? You’re not alone!
SPF, or sun protection factor, is the number you see on almost every sunscreen product. But what does it really mean, and why is it so important for sun safety? Understanding SPF is not just a step, but a powerful tool to protect your skin from sunburn, premature aging, and even skin cancer. Whether you’re on a beach day, a city stroll, or just running errands, knowing what SPF actually does can empower you to make smarter choices for your skin.
In this guide, you’ll find SPF explained—from what the SPF number tells you, to how it works, how much sunscreen to use, and how to choose the best protection for your lifestyle. Because sun protection isn’t just for summer; it’s a year-round responsibility for everyone, regardless of skin type or where you live. Being proactive about sun protection is a key part of your health and skincare routine.
Let’s demystify SPF sunscreen once and for all, so you can confidently pick the right sunscreen, apply it properly, and get the best protection against UV rays—every single day.

What Does SPF Stand For?
SPF stands for Sun Protection Factor. It’s the official way sunscreen products tell you how well they help protect your skin from sunburn, which is mostly caused by UVB rays—the part of UV radiation that’s especially sneaky when it comes to burning fair-skinned folks and increasing the risk of skin cancer.
Here’s what the SPF number actually means:
If you use the amount of sunscreen recommended by experts and apply sunscreen evenly, the SPF value is an indicator of how much more sun exposure your skin can handle without burning, compared to bare skin. For example, SPF 30 means your sunscreen provides 30 times the level of sunburn protection provided by no sunscreen at all. If you’d burn after 10 minutes in direct sun, SPF 30 could, in theory, let you stay in the sun for about 300 minutes before burning—but only under perfect conditions.
SPF explained simply:
- SPF 15 sunscreen allows about 1/15th of the sun’s UVB rays to reach your skin (it filters out about 93%)
- SPF 30 filters about 97%
- SPF 50 blocks roughly 98%
But here’s the truth: it is not directly related to time in the sun, because things like intensity of sunlight, amount of sunscreen applied, sweating, swimming, and your geographic location all change how long you’re protected. Plus, no sunscreen is a suit of armor—so you still need to reapply every two hours or after swimming and sweating.
So, next time you look at that SPF rating, remember: it’s an indicator of the level of protection your sunscreen offers—nothing more, nothing less!
How Does SPF Work?
Let’s break down how SPF sunscreen actually protects your skin.
It is all about blocking or absorbing the UVB rays that cause sunburn and, over time, can lead to skin cancer. When you apply sunscreen, the active ingredients (whether mineral or chemical) create a barrier that either absorbs, reflects, or scatters UV radiation before it can damage your skin.
- Mineral sunscreens (like those with zinc oxide or titanium dioxide) sit on top of your skin and act like tiny mirrors, reflecting UV rays away.
- Chemical sunscreens use active ingredients that absorb UVB rays and transform them into harmless heat.
But SPF doesn’t tell the whole story! While the SPF value is a measure of how much UVB protection you’re getting, it doesn’t say anything about UVA protection. UVA rays are the ones that penetrate deeper, causing skin aging and contributing to some cancers. That’s why it’s crucial to choose a broad spectrum sunscreen, which offers protection against both UVA and UVB rays.
Here’s a simple analogy:
If your skin would normally start to burn after 10 minutes of sun exposure, using SPF 30 (with the correct amount of sunscreen applied) theoretically allows you to stay in the sun 30 times longer—about 300 minutes—before burning. But don’t let the math fool you: the intensity of sunlight, the amount of sunscreen you use, sweating, and even your geographic location can all change how well your sunscreen protects.
Quick chart:
SPF ValueUVB Protection
SPF 15 ~93%
SPF 30 ~97%
SPF 50 ~98%
SPF 100 ~99%
Bottom line: No sunscreen is perfect, so reapply every two hours, especially after you sweat or swim. This is because sunscreen can wear off or be rubbed off, reducing its effectiveness. For the best protection, combine sunscreen with protective clothing, hats, and shade—especially during peak sun intensity!
Types of UV Rays: UVA vs. UVB
Not all UV rays are created equal—understanding the difference between UVA and UVB is the key to real sun protection.
- UVB rays are the main culprits behind sunburn. They’re strongest from late morning to mid-afternoon and change in intensity depending on your geographic location and season. UVB radiation is also the main focus of most SPF numbers—so when you see a sunscreen labeled SPF 30, it’s all about blocking those UVB rays and preventing sunburn.
- UVA rays penetrate deeper into the skin and are sneaky: they’re present all day, all year, and they go right through clouds and even glass. UVA is responsible for skin aging (think wrinkles and sun spots) and contributes to skin cancer.
That’s why you want a broad spectrum sunscreen—it protects against both UVA and UVB radiation, giving you a more complete shield. Sunscreen products labeled ‘broad spectrum’ have been tested to ensure they protect your skin from a wider spectrum of harmful rays, not just sunburn. This means they provide protection against both UVA and UVB rays, reducing the risk of skin aging and skin cancer.
Quick summary:
- UVB = Burning (sunburn)
- UVA = Aging (wrinkles, dark spots)
- Both = Skin cancer risk
Pro tip: Always choose a sunscreen with broad-spectrum on the label for the best protection—especially for your face, where both aging and burning matter most.
How Much SPF Do You Really Need?
Here’s the truth: dermatologists and the FDA recommend using a minimum SPF of 30 for everyday sun protection. SPF 30 filters out about 97% of UVB rays, which is usually enough for daily wear—whether you’re walking the dog or grabbing coffee outside. But is higher SPF always better?
Let’s bust some myths:
- SPF 50 blocks about 98% of UVB radiation—only a slight bump from SPF 30.
- SPF 100 filters around 99%. Sounds impressive, right? But no sunscreen can block 100% of UV rays, no matter how high the SPF rating.
- A higher SPF isn’t a free pass to stay in the sun all day. Most people don’t apply enough sunscreen, and very few reapply every two hours (or after swimming/sweating)—which the FDA says is essential for best protection.
How much sunscreen should you use?
- The standard “one ounce” (about a shot glass) covers the whole body for one application.
- For your face and neck, use a generous quarter-sized blob.
- Reapply every two hours, or right after you swim or sweat—even if your sunscreen is labeled “water resistant” (typically for 40 or 80 minutes).
Bottom line:
- Choose at least SPF 30 for everyday use.
- For long days outside, fair-skinned or melanin-rich skin, or intense sun exposure, SPF 50 or higher can help—but only if you use enough, and reapply often.
- Know that SPF is not directly related to safe “time in the sun”; it’s about the amount of solar energy your skin can handle.
So, don’t get caught up in chasing the highest number. Focus on applying enough sunscreen, reapplying, and combining sun protection with shade and protective clothing for the best level of sunburn protection.
How to Choose the Right SPF for Your Skin
Picking the right SPF sunscreen isn’t about finding the “perfect” number, but matching your level of protection to your skin type, daily routine, and sun exposure. Here’s what matters most:
For Face vs. Body
- The best SPF for face is at least SPF 30—bonus if it’s non-comedogenic (won’t clog pores).
- For your body, use SPF 30 or higher, and don’t forget often-missed spots like ears, hands, and feet.
By Activity & Climate
- Beach, hiking, sports, or intense sun? Go with SPF 50 or higher, water resistant, and reapply every two hours (or after 40/80 minutes of swimming or sweating).
- City, office, or mostly indoors? SPF 30 is usually enough, but don’t skip sunscreen—UV rays can come through windows and even on cloudy days.
Special Cases
- Sensitive skin: Mineral sunscreens (zinc oxide, titanium dioxide) are gentle, low-irritation, and give broad spectrum protection.
- Kids and babies: Always use broad-spectrum, mineral sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher; their skin is more vulnerable to UV radiation.
- Post-procedure or fair-skinned: Choose higher SPF, broad-spectrum, and reapply with care.
- Melanin-rich skin: All skin tones can get sunburn and skin cancer, so SPF 30 or above is a must for safe, glowing skin.
Quick Checklist
- Broad spectrum on the label? ✔️
- SPF 30 or higher? ✔️
- Water resistant if swimming or sweating? ✔️
- Reapply every two hours or after water/sweat? ✔️
Don’t forget: Even the best SPF sunscreen can’t do its job if you don’t apply enough or forget to reapply! Combine SPF with shade, hats, and protective clothing for true sun safety.
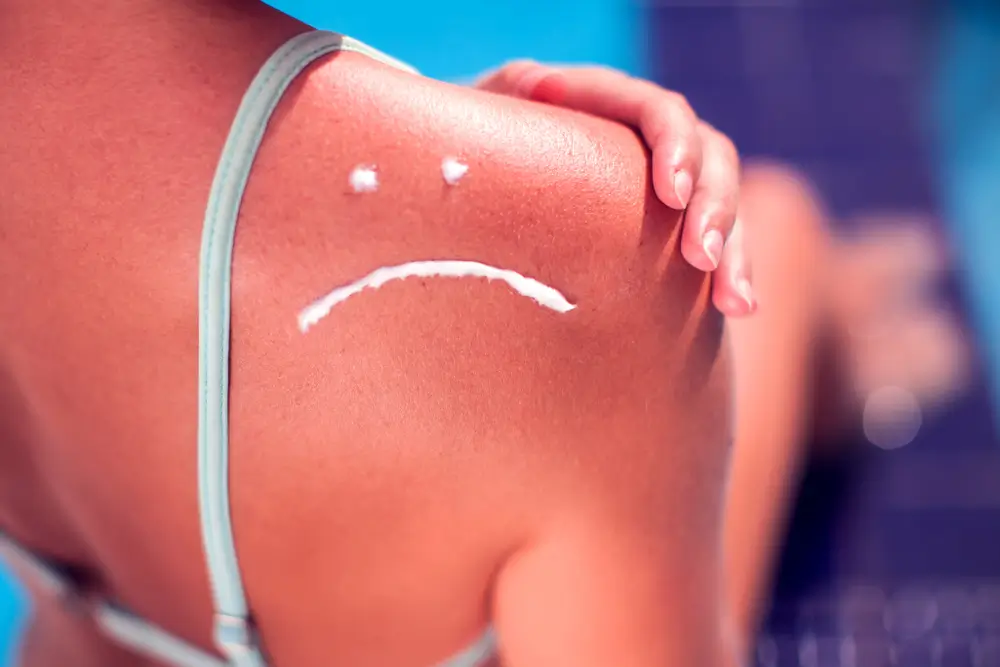

SPF in Natural and Mineral Sunscreens
Not all sunscreens are created equal—especially when it comes to “natural” or mineral sunscreen. These formulas use active ingredients like zinc oxide and titanium dioxide to block or scatter both UVB and UVA rays. Mineral sunscreens are often called “physical sunscreens” because they sit on the skin’s surface and act like tiny shields, rather than being absorbed.
Wondering how mineral formulas stack up against chemical options? My ultimate mineral sunscreen breakdown covers everything from ingredients to application tricks, while the in-depth guide to chemical sunscreen explains how chemical filters work and who they’re best for. For the full side-by-side, see my Mineral vs. Chemical Sunscreen comparison.
How does SPF work in mineral sunscreen?
The SPF value on mineral sunscreen still measures UVB protection—the same way it does for chemical sunscreens. For example, an SPF 30 mineral sunscreen filters about 97% of UVB rays, just like its chemical cousin. The bonus? Most mineral formulas naturally provide broad spectrum coverage, giving you protection from both burning (UVB) and aging (UVA) rays.
Tips for choosing mineral sunscreen:
- Look for “broad spectrum” (protects from UVA & UVB)
- Check for zinc oxide and/or titanium dioxide in active ingredients
- Apply sunscreen generously and reapply every two hours, especially after swimming or sweating
For even more tips on safe sun habits, explore my sun protection essentials and build a routine that truly protects your skin.
Common SPF Myths & FAQs
What does SPF stand for?
SPF stands for Sun Protection Factor. It’s the number you see on sunscreen bottles and is a measure of how well a sunscreen protects your skin from UVB rays—the kind of radiation that causes sunburn and increases the risk of skin cancer.
What SPF should I use—and is SPF 30 or 50 better?
For daily sun safety, dermatologists and the FDA recommend at least SPF 30. SPF 30 blocks about 97% of UVB rays, while SPF 50 blocks around 98%. The difference in protection is small, so the best SPF is the one you’ll apply generously and reapply every two hours.
Is SPF 100 better than SPF 50?
Not really—SPF 100 filters about 99% of UVB radiation, compared to 98% for SPF 50. No sunscreen provides 100% protection, so don’t rely just on a higher SPF. Focus on applying enough sunscreen and reapplying often for the best sun protection.
Will SPF 30 prevent sunburn?
Yes, if you use the right amount of sunscreen and reapply as directed, SPF 30 sunscreen provides strong sunburn protection for most people. But remember, fair-skinned and sensitive skin may need to be extra careful, and intense sun or sweating can decrease protection—so stay consistent.
Is SPF for UVA or UVB?
SPF measures protection against UVB rays (the “burning” rays). For the best protection, always choose a broad-spectrum sunscreen that also blocks UVA rays, which cause premature aging and contribute to skin cancer.
How to Apply SPF Properly
You’ve picked your SPF 30 or SPF 50 sunscreen—now let’s make sure you get the best protection from it!
How much sunscreen should you use?
Most adults need about one ounce of sunscreen (think: a full shot glass) to cover their body properly. For your face and neck alone, use a generous, even layer—don’t skimp!
When and how often should you apply sunscreen?
- Apply sunscreen 15 minutes before heading outside.
- Reapply every two hours—and always after swimming, sweating, or towel-drying, even if your sunscreen is labeled water resistant (that usually means protection for 40 or 80 minutes during water or sweat).
Tips for the best protection:
- Don’t forget often-missed spots: ears, the back of your neck, hands, tops of feet, and the hairline.
- If you’re using other skincare or makeup, SPF should always be your last step (unless your dermatologist says otherwise).
- For outdoor sports, beach days, or intense sun, consider extra protective clothing and shade in addition to sunscreen products.
**Sun safety isn’t just about the SPF number—**it’s about the way sunscreen is applied and reapplied. Consistency and proper use make all the difference in protecting your skin from UV rays, sunburn, and long-term damage.
Extra Protection: What To Look For On Your Sunscreen Label
| Label/Term | What It Means | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Broad Spectrum | Protects against both UVA (aging) and UVB (burning) rays | For the best protection against sunburn, skin cancer, and aging |
| PA Rating (PA+ to PA++++) | Measures the level of UVA protection (more “+” means higher protection) | Especially important for anti-aging and all-day sun safety |
| Water Resistant | SPF stays effective for 40 or 80 minutes during water or sweat | Still need to reapply after swimming, sweating, or towel-drying |
| Antioxidants | Boosts sunscreen’s ability to fight free radicals and blue light | Helps protect your skin beyond just UV rays |
| Protective Clothing | Physical sun barriers: hats, UPF shirts, sunglasses | Extra sun protection for long days outdoors or when sunscreen wears off |
Pro tip:
Always check your sunscreen label for broad-spectrum and SPF 30 or higher. For outdoor adventures, look for “water resistant,” and add protective clothing for the ultimate sun safety routine!
KM’s Pro Tips for Smart Sun Protection
- Make sunscreen a habit, not a hassle. Keep your favorite SPF sunscreen by the door, in your bag, or even at your desk so you never forget to reapply—especially if you’re in and out during the day.
- Apply sunscreen to more than just your face! Ears, neck, scalp part, lips, hands, and feet all need sun protection. Fair-skinned or melanin-rich, everyone benefits from SPF.
- Use enough: Most people use too little. For best protection, use at least one ounce (about a shot glass) for your body, and a nickel-sized amount for your face.
- Double up: On extra sunny days, pair your sunscreen with protective clothing, hats, and sunglasses for the best sun safety.
- Reapply every two hours—or immediately after sweating, swimming, or toweling off. No SPF lasts all day, no matter how high the SPF number.
- After-sun care matters. Treat your skin to gentle, soothing ingredients like aloe, chamomile, or try my DIY after-sun recipes for healthy, hydrated skin.
Want a sun care routine tailored to you? Discover my top best sunscreen habits for every skin type—because smart sun protection is all about what works for you, every day.
Conclusion: Your Next Steps for Safe, Glowing Skin
Understanding SPF is the first step toward real, year-round sun protection. Remember, the best sunscreen is the one you’ll actually use—generously and consistently. Whether you choose mineral or chemical, SPF 30 or SPF 50, what matters most is applying the right amount, reapplying every two hours, and choosing broad-spectrum formulas for full UVA and UVB defense.
Ready to step up your sun safety game?
Explore my detailed guides on mineral sunscreen, chemical sunscreen, mineral vs. chemical sunscreen, sun protection habits, and my new must-read: best sunscreen habits for every skin type.
If you have questions or want to share your favorite SPF routine, drop a comment below. Your skin will thank you for every little step you take towards smarter sun care! 🌞
Kristina